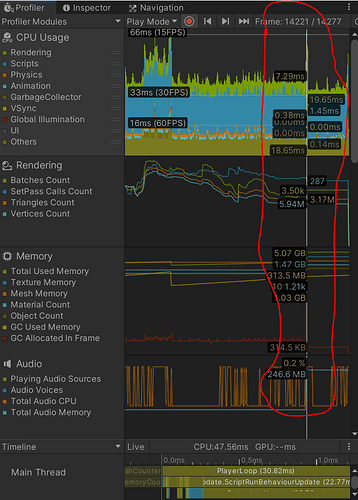
Hello all, @Brian_Trotter I have a new topic I need some help with
When dialogues get too big, let’s say for a massive quest or something, there’s usually a big performance bottleneck attached to it, and the ‘Next’ button, and firing the dialogue up the first time, can be a little expensive at times as a result.
I have identified areas that can be improved but no matter what I try, it doesn’t seem to boost the performance at all
My latest attempt was like the LazyValue approach for the health of the player and NPCs. In simple terms, only cache/process the nodes that come next and ignore everything else as a way to boost performance, and it seems like a great idea for dialogues that can go insanely big, but… implementing that has been very challenging, and that’s where I need help
So, in a nutshell, my current problem is:
a. Firing up a dialogue with 20+ nodes is very slow and expensive performance wise
b. The ‘Next’ button for that dialogue is also usually slow and expensive performance wise
These are the 2 problems I want to solve at any cost
I will attach 3 different scripts below, hopefully they all come to good use
- Dialogue.cs:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor; // to be able to access the 'Undo' class (line 81)
namespace RPG.Dialogue {
[CreateAssetMenu(fileName = "New Dialogue", menuName = "Dialogue", order = 0)]
public class Dialogue : ScriptableObject, ISerializationCallbackReceiver // ISerializationCallbackReceiver Interface avoids errors in Adding object to asset (line 90)
{
[SerializeField]
List<DialogueNode> nodes = new List<DialogueNode>();
[SerializeField]
Vector2 newNodeOffset = new Vector2(250, 0);
// key = string, value = DialogueNode (Dictionaries are used because of their ability to quickly find value of stuff, based on given keys)
Dictionary<string, DialogueNode> nodeLookup = new Dictionary<string, DialogueNode>();
private void Awake()
{
// Whilst OnValidate() is always called in the '#if UNITY_EDITOR' -> '#endif' range, it never
// gets called outside of the Unity Editor. The result? Our 'NEXT' button for our game dialogues was never exported
// (because to the game, it's NEVER called).
// To fix that, we call it in Awake(), as shown below (this calls ALL OnValidate() functions, under all scripts
// with the same namespace as this one ('RPG.Dialogue' in this case)):
OnValidate();
}
private void OnValidate()
{
nodeLookup.Clear();
foreach (DialogueNode node in GetAllNodes())
{
nodeLookup[node.name] = node;
}
}
public IEnumerable<DialogueNode> GetRootNodes()
{
foreach (DialogueNode node in GetAllNodes())
{
bool isChild = false;
foreach (DialogueNode lookupNode in GetAllNodes())
{
if (lookupNode.GetChildren().Contains(node.name))
{
isChild = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isChild) yield return node;
}
}
// IEnumerables are an Interface (of type 'Dialogue Nodes' in this case), allowing objects to do 'for' loops over them:
public IEnumerable<DialogueNode> GetAllNodes()
{
return nodes;
}
public DialogueNode GetRootNode()
{
return nodes[0];
}
public IEnumerable<DialogueNode> GetAllChildren(DialogueNode parentNode)
{
List<DialogueNode> result = new List<DialogueNode>();
foreach (string childID in parentNode.GetChildren())
{
if (nodeLookup.ContainsKey(childID))
{
yield return nodeLookup[childID];
}
}
}
// TEST FUNCTION - 19/5/2024:
public static Dialogue GetByName(string dialogueName)
{
foreach (Dialogue dialogue in Resources.LoadAll<Dialogue>(""))
{
if (dialogue.name == dialogueName)
{
return dialogue;
}
}
return null;
}
#if UNITY_EDITOR
public void CreateNode(DialogueNode parent)
{
DialogueNode newNode = MakeNode(parent);
Undo.RegisterCreatedObjectUndo(newNode, "Created Dialogue Node");
Undo.RecordObject(this, "Added Dialogue Node");
AddNode(newNode);
}
public void DeleteNode(DialogueNode nodeToDelete)
{
Undo.RecordObject(this, "Deleted Dialogue Node");
nodes.Remove(nodeToDelete);
OnValidate();
CleanDanglingChildren(nodeToDelete); // cleans up children (further nodes connected to node to delete down the line) of parent nodes that have been deleted
Undo.DestroyObjectImmediate(nodeToDelete); // destroys our node (but also saves a backup, just in case you need to Undo your changes)
}
private DialogueNode MakeNode(DialogueNode parent)
{
DialogueNode newNode = CreateInstance<DialogueNode>();
newNode.name = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
if (parent != null)
{
parent.AddChild(newNode.name);
newNode.SetPlayerSpeaking(!parent.IsPlayerSpeaking());
newNode.SetPosition(parent.GetRect().position + newNodeOffset);
}
return newNode;
}
private void AddNode(DialogueNode newNode)
{
nodes.Add(newNode);
OnValidate();
}
private void CleanDanglingChildren(DialogueNode nodeToDelete)
{
foreach (DialogueNode node in GetAllNodes())
{
node.RemoveChild(nodeToDelete.name);
}
}
#endif
public void OnBeforeSerialize()
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
if (nodes.Count == 0)
{
DialogueNode newNode = MakeNode(null);
AddNode(newNode);
}
// For saving files on the Hard Drive
if (AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(this) != "") {
foreach(DialogueNode node in GetAllNodes()) {
if (AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(node) == "") {
// For Loading a file off the Hard Drive/SSD
AssetDatabase.AddObjectToAsset(node, this); // adds the new nodes in the same dialogue under the original Dialogue Node
}
}
}
#endif
}
public void OnAfterDeserialize()
{
// Without this function, even if it's empty, the 'ISerializationCallbackReceiver' interface will stop the
// game from running
}
public IEnumerable<DialogueNode> GetPlayerChildren(DialogueNode currentNode)
{
foreach (DialogueNode node in GetAllChildren(currentNode)) {
if (node.IsPlayerSpeaking()) {
yield return node;
}
}
}
public IEnumerable<DialogueNode> GetAIChildren(DialogueNode currentNode)
{
foreach(DialogueNode node in GetAllChildren(currentNode)) {
if (!node.IsPlayerSpeaking())
{
yield return node;
}
}
}
}
}
- DialogueUI.cs:
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
using RPG.Dialogue;
using TMPro;
using GameDevTV.UI; // so we can use 'ShowHideUI.cs' to deactivate the Dialogue when the game is paused
namespace RPG.UI
{
public class DialogueUI : WindowController
{
PlayerConversant playerConversant;
[SerializeField] TextMeshProUGUI AIText;
[SerializeField] Button nextButton;
[SerializeField] GameObject AIResponse;
[SerializeField] Transform choiceRoot;
[SerializeField] GameObject choicePrefab;
[SerializeField] Button quitButton; // quit button, to quit the dialogue midway through
[SerializeField] TextMeshProUGUI conversantName; // name of our conversant in a dialogue conversation
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
nextButton.onClick.AddListener(() => playerConversant.Next()); // calls the 'Next' function (yes, the function not a variable) Subscriber (to the onClick event) when our player hits 'Next' in the dialogue, using the Lambda "() => {}" function
quitButton.onClick.AddListener(() => playerConversant.Quit()); // Lambda Function, "() => {}", is used here to add a listener for our quit button. When clicked the script is closed
// ShowHideUI.OnModalActive += playerConversant.Quit; // Turn off the Dialogue UI when the game is paused
UpdateUI();
}
// ShowHideUI.OnModalActive is a static event, hence this function is mandatory:
void OnDestroy()
{
// ShowHideUI.OnModalActive -= playerConversant.Quit;
}
// Update is called once per frame
void UpdateUI()
{
/* Debug.Log($"UpdateUI playerConversant.IsActive() == {playerConversant.IsActive()}");
gameObject.SetActive(playerConversant.IsActive());
if (!playerConversant.IsActive())
{
Debug.Log("Exiting DialogueUI as playerConversant is not active");
return;
}
Debug.Log("Continuing with DialogueUI as playeConversant is active");
//rest of method */
// The following line ensures the dialogue is invisible until the return time
// of the IEnumerator in 'playerConversant.cs' time counter is over
gameObject.SetActive(playerConversant.IsActive());
if (!playerConversant.IsActive())
{
return;
}
conversantName.text = playerConversant.GetCurrentConversantName();
AIResponse.SetActive(!playerConversant.IsChoosing());
choiceRoot.gameObject.SetActive(playerConversant.IsChoosing());
if (playerConversant.IsChoosing())
{
BuildChoiceList();
}
else
{
AIText.text = playerConversant.GetText();
nextButton.gameObject.SetActive(playerConversant.HasNext());
}
}
private void BuildChoiceList()
{
foreach (Transform item in choiceRoot)
{
// avoids Dangling Nodes in the Hierarchy, which will eventually slow our entire game down
Destroy(item.gameObject);
}
foreach (DialogueNode choice in playerConversant.GetChoices())
{
GameObject choiceInstance = Instantiate(choicePrefab, choiceRoot);
var textComp = choiceInstance.GetComponentInChildren<TextMeshProUGUI>();
textComp.text = choice.GetText();
Button button = choiceInstance.GetComponentInChildren<Button>();
button.onClick.AddListener(() =>
{ // "() => {}" is a 'lambda' function ("()" is the argument, "{}" is the internals of the function), which only works when a button is clicked (do some research about this)
playerConversant.SelectChoice(choice);
});
}
}
protected override void Subscribe()
{
playerConversant = GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("Player").GetComponent<PlayerConversant>();
playerConversant.onConversationUpdated += UpdateUI;
}
protected override void Unsubscribe()
{
playerConversant.onConversationUpdated -= UpdateUI;
}
protected override void OnDisable()
{
base.OnDisable();
playerConversant.Quit();
}
}
}
- PlayerConversant.cs (for the Next button):
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using System.Linq;
using System;
using RPG.Core; // for the Evaluator of the Dialogues (line 133)
using RPG.Movement;
using GameDevTV.Utils;
namespace RPG.Dialogue {
public class PlayerConversant : MonoBehaviour, IAction
{
[SerializeField] string playerName;
Dialogue currentDialogue;
DialogueNode currentNode = null;
AIConversant currentConversant = null; // the conversation being occured between the Player and the AI (to trigger events during the conversation for instance)
bool isChoosing = false;
// OUT OF COURSE CONTENT ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
private Dialogue targetDialogue; // the Dialogue our Player is aiming to go to, for conversation purposes
private AIConversant targetConversant; // the Target Conversant of our Quest Giver = Player Conversant
public float acceptanceRadius; // the minimum distance our Player has to be from the NPC before they can talk
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public event Action onConversationUpdated;
public void StartDialogue(AIConversant newConversant, Dialogue newDialogue) {
// TEST (Delete if failed):
if (newConversant == currentConversant) return;
currentConversant = newConversant;
currentDialogue = newDialogue;
currentNode = currentDialogue.GetRootNode();
TriggerEnterAction();
onConversationUpdated(); // this line subscribes our Dialogue to the event Action we created above, so that it follows along when something new to that event occurs
}
public void Quit() {
// When the conversation is over, or the 'X' button is clicked, this function is called
currentDialogue = null; // no node available
TriggerExitAction();
// Test
/* Debug.Log("Quit Dialogue - Before TriggerExitAction");
TriggerExitAction();
Debug.Log("Quit Dialogue - After TriggerExitAction"); */
currentNode = null; // no Nodes available to process through
isChoosing = false; // no choices of conversations available
currentConversant = null; // quitting the AI Conversant Dialogue
onConversationUpdated(); // makes the dialogue hide itself when the chat is over
}
// Current Conversant (lambda, 'on the fly' function), which will deactivate the NPC walking around when our player starts talking to him:
public AIConversant GetCurrentConversant() => currentConversant;
public bool IsActive() {
// This function (a 'getter' function) returns whether we have a current Dialogue to refer to (after the 2 seconds of the IEnumerator)
return currentDialogue != null;
}
public bool IsChoosing() {
// getter
return isChoosing;
}
public string GetText() {
// getter
if (currentDialogue == null) {
return "";
}
return currentNode.GetText();
}
public IEnumerable<DialogueNode> GetChoices() {
return FilterOnCondition(currentDialogue.GetPlayerChildren(currentNode));
}
public void SelectChoice(DialogueNode chosenNode) {
currentNode = chosenNode;
TriggerEnterAction();
isChoosing = false;
// OPTIONAL: Implement this line only if you don't want the next conversation to display what your button just had written on it:
Next();
// if we didnt call 'Next()', which calls 'onConversationUpdated()' event subscription, we could've called it here instead
}
public void Next() {
int numPlayerResponses = FilterOnCondition(currentDialogue.GetPlayerChildren(currentNode)).Count();
if (numPlayerResponses > 0) {
isChoosing = true;
TriggerExitAction();
onConversationUpdated();
return;
}
DialogueNode[] children = FilterOnCondition(currentDialogue.GetAIChildren(currentNode)).ToArray(); // filters our Player <-> Quest Giver responses based on the process of our Quests
int randomIndex = UnityEngine.Random.Range(0, children.Count()); // UnityEngine is mentioned here because Random.Range comes from both UnityEngine and System (which we need for event Action), hence we need to specify which function we are calling
TriggerExitAction();
currentNode = children[randomIndex];
TriggerEnterAction();
onConversationUpdated();
}
public bool HasNext() {
return FilterOnCondition(currentDialogue.GetAllChildren(currentNode)).Count() > 0;
}
private IEnumerable<DialogueNode> FilterOnCondition(IEnumerable<DialogueNode> inputNode) {
// This function ensures we can play different Nodes on our dialogues, based on the Progress Status of our Quests (Start, Pending, Complete, etc)
foreach (var node in inputNode) {
if (node.CheckCondition(GetEvaluators())) {
yield return node; // if a condition (E.g: A quest has been done) is met, we include it in our filter, otherwise it's excluded from the Filter
}
}
}
private IEnumerable<IPredicateEvaluator> GetEvaluators() {
return GetComponents<IPredicateEvaluator>();
}
private void TriggerEnterAction() {
if (currentNode != null) {
TriggerAction(currentNode.GetOnEnterAction());
}
}
private void TriggerExitAction() {
if (currentNode != null)
{
TriggerAction(currentNode.GetOnExitAction());
}
}
private void TriggerAction(string action) {
if (action == "") return;
foreach(DialogueTrigger trigger in currentConversant.GetComponents<DialogueTrigger>()) {
trigger.Trigger(action);
}
}
public string GetCurrentConversantName()
{
if (isChoosing) {
return playerName;
}
else {
return currentConversant.GetName();
}
}
// MORE OUT OF COURSE CONTENT (RUNNING TO CLICKED NPC BEFORE INTERACTING IN DIALOGUE WITH THEM) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
public void Cancel()
{
Quit(); // if you cancel a dialogue, you just Quit it...
targetConversant = null; // ... and you also ensure that you're not talking to anyone in-game
}
public void StartConversation(AIConversant conversant, Dialogue dialogue) {
GetComponent<ActionSchedular>().StartAction(this);
targetConversant = conversant;
targetDialogue = dialogue;
}
void Update() {
if (!targetConversant) return;
if (Vector3.Distance(transform.position, targetConversant.transform.position) > acceptanceRadius) {
// transform.LookAt(targetConversant.transform);
GetComponent<Mover>().MoveTo(targetConversant.transform.position, 1.0f);
}
else {
GetComponent<Mover>().Cancel();
StartDialogue(targetConversant, targetDialogue);
targetConversant = null; // stops our player from being a creepy stalker that creepily follows the NPCs around
}
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
}